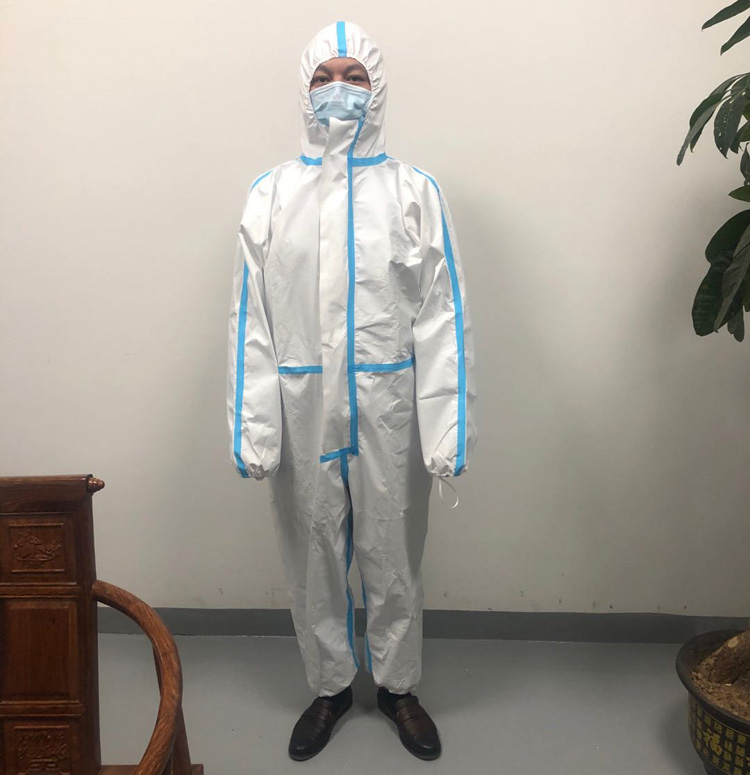
Medical protective clothing
Medical protective clothing refers to protective clothing used by medical personnel (doctors, nurses, public health personnel, cleaning staff, etc.) and people entering specific medical and health areas (such as patients, hospital visitors, personnel entering infected areas, etc.). Its role is to isolate bacteria, harmful ultra-fine dust, acid and alkali solutions, electromagnetic radiation, etc., to ensure the safety of personnel and keep the environment clean.

Classification
Medical protective clothing includes various types of clothing specially worn in a medical environment, so there are many classification methods.
1.Classified by purpose
According to the purpose and use occasion, it can be divided into: daily work clothes, surgical clothes, isolation clothing and protective clothing.
Daily work clothes refer to white coats, also called white coats, worn by medical staff in their daily work.
Surgical suits are specially designed garments worn in the operating room.
Isolation clothing refers to clothing worn by medical personnel when they are in contact with patients, family members visiting patients, and so on.
Protective clothing refers to clothing worn by persons in medical emergency, special areas such as infectious disease areas, and electromagnetic radiation areas.
- Classified by service life
Medical protective clothing can be divided into disposable protective clothing and reusable protective clothing according to the service life.
Disposable protective clothing is discarded after use without disinfection and washing. It is easy to use and can avoid cross infection. However, the degradation of disposable materials is slow and it is easy to cause environmental pollution. This type is usually used for surgical operation clothes and isolation clothes with high protective requirements.
Reusable types require measures such as washing and high-temperature disinfection after use. Generally, the comfort of the material is better, but the protective performance is usually poor. The washing and disinfecting process will also increase a lot of manpower and water resources costs,This type is usually used for daily work clothes (white coats) with less protective requirements.
- Classified by material
According to different materials processing technology, medical protective clothing is divided into woven and non-woven protective clothing.
Woven materials are mainly used to process reusable medical protective clothing, including traditional woven fabrics, high-density fabrics, coated fabrics and laminated fabrics. Traditional woven fabrics are mainly made of cotton fiber or polyester and other synthetic fibers and cotton blended yarns, which have good comfort and are mainly used in daily work clothes (white coats). High-density fabrics are made of high-count cotton yarns or other ultra-fine synthetic fiber filaments. The yarn gap is very small. Because of the capillary action of the fibers, they have moisture permeability. After treatment with fluorocarbon, silicone and other waterproofing agents, it has a certain resistance to liquid penetration. It is mainly used for surgical gown materials that need better waterproof effect.. Coated and laminated fabrics are used to enhance the material's permeability resistance and are used in protective clothing materials in harsh environments. The coated fabric is processed by coating, the surface is closed by the coating agent, and has the permeability resistance. The hydrophilic groups in the coating or the microporous structure formed by special methods ensure the fabric's moisture permeability. Laminated fabric is a composite of a fabric and a layer of special film (such as a microporous film, a polyurethane moisture-permeable film, etc.) through a lamination process, such as a polytetrafluoroethylene super waterproof and moisture-permeable composite fabric. Because the pore diameter of the microporous membrane of the fabric is much smaller than the diameter of water droplets, it can prevent the penetration of blood, body fluids, etc. The high porosity of the micropores is larger than the diameter of water vapor molecules, and water vapor molecules can pass freely, so the moisture permeability is better.
Non-woven protective clothing materials are basically disposable, and more commonly used are spunbond nonwovens, spunlace nonwovens, SMS (spunbond-meltblown-spunbond) composite nonwovens, and flash evaporation. Non-woven fabrics and spunbond fabric lamination products. Generally, non-woven protective clothing has better protection than mechanical materials.
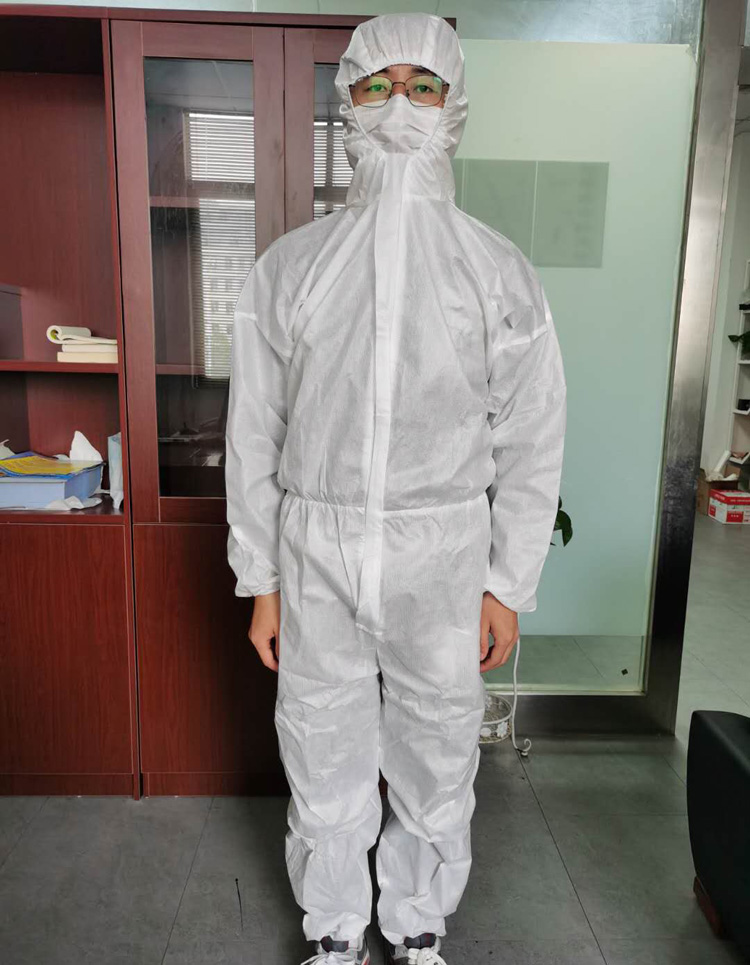

Performance requirements
In addition to the specifications and safety requirements of the material itself, the performance of medical protective clothing mainly includes aspects such as protection, comfort, and physical and mechanical properties.
- Protective
Protective properties are the most important performance requirements of medical protective clothing, including liquid barriers, microbial barriers, and barriers to particulate matter.
Liquid barrier means that medical protective clothing should be able to prevent the penetration of liquids such as water, blood, alcohol, etc., and have a hydrophobicity of level 4 or higher to avoid contamination of clothing and human body. Prevent the blood, body fluids and other secretions of the patient from transmitting the virus to the medical staff during the operation.
Microbial barriers include barriers to bacteria and viruses. The barrier to bacteria is mainly to prevent contact transmission (and back propagation) of medical personnel to the patient's surgical wound during the surgery. The virus barrier is mainly to prevent the medical staff from contacting the patient's blood and body fluids, and the virus carried in it causes cross infection between doctors and patients.
Particulate matter barrier refers to preventing viruses transmitted through the air from being inhaled or attached to the skin surface and absorbed by the body in the form of aerosols.
- Comfort performance
Comfort includes breathability, water vapor permeability, drapability, quality, surface thickness, electrostatic properties, color, reflectivity, odor, and skin sensitization.The most important is breathability and moisture permeability.The most important is breathability and moisture permeability. In order to enhance the protective effect, protective clothing fabrics are usually laminated or coated, resulting in heavy, breathable and poor moisture permeability. Long-term wear is not conducive to sweat and heat dissipation.The antistatic requirement is to prevent the static electricity in the operating room, which will cause the surgical gown to absorb a large amount of dust and bacteria, which is not good for the patient's wounds, and at the same time to prevent sparks generated by static electricity from detonating volatile gases in the operating room and affecting the accuracy of precision instruments
- Physical and mechanical properties
Physical and mechanical properties mainly refer to the ability of medical protective clothing materials to resist tearing, puncture and abrasion. Avoid tears and punctures to provide a channel for bacteria and viruses to spread, and abrasion resistance can prevent flocs from providing a place for bacteria and viruses to reproduce.
- Other properties
In addition to the properties listed above, medical protective clothing must also have disinfection resistance, good color fastness to washing, prevention of shrinkage, No combustion supporting, non-toxicity and non-irritation, and harmless to the skin.

Special medical protective clothing
- Chemical protective clothing
Chemical protective clothing is protective clothing worn to protect yourself from chemical dangers or corrosive substances when handling hazardous medical chemicals.Chemical protective clothing requires not only chemical corrosion resistance of clothing materials, but also more strict requirements on sealing and seam structure of clothing.
- Electromagnetic radiation protective clothing
Electromagnetic radiation protective clothing is a protective clothing that implants extremely fine conductive fibers in the fabric material, so that the protective clothing does not generate static electricity and can shield electromagnetic waves in the range of 100kHz to 300GHz. Mainly used for operating people of electronic medical equipment systems in hospitals
- Nuclear and radiation protective clothing
It is used in nuclear radiation environment (small-dose, large-scale ionizing radiation, mainly α, β-rays), to prevent the invasion of human bodies by radio aerosols and dust. It has the functions of protecting radioactive aerosols, protecting more than 150 kinds of toxic and corrosive gases, liquids and solids, protecting potential radioactive particles and liquids from entering the body, and 100% blocking dry particles of more than 0.2 μm.